SUMMARY: Who’s Building AI Data Centers?
- Hyperscale Leaders: Microsoft ($80B investment), Amazon AWS, Google, and Meta are committing massive capital to AI-specific facilities.
- GPU Specialists: CoreWeave ($12B funding), Crusoe Energy, and Lambda Labs focus exclusively on AI workloads with specialized infrastructure.
- Traditional Adapters: Digital Realty, Equinix, and Oracle are retrofitting existing capabilities for AI demands.
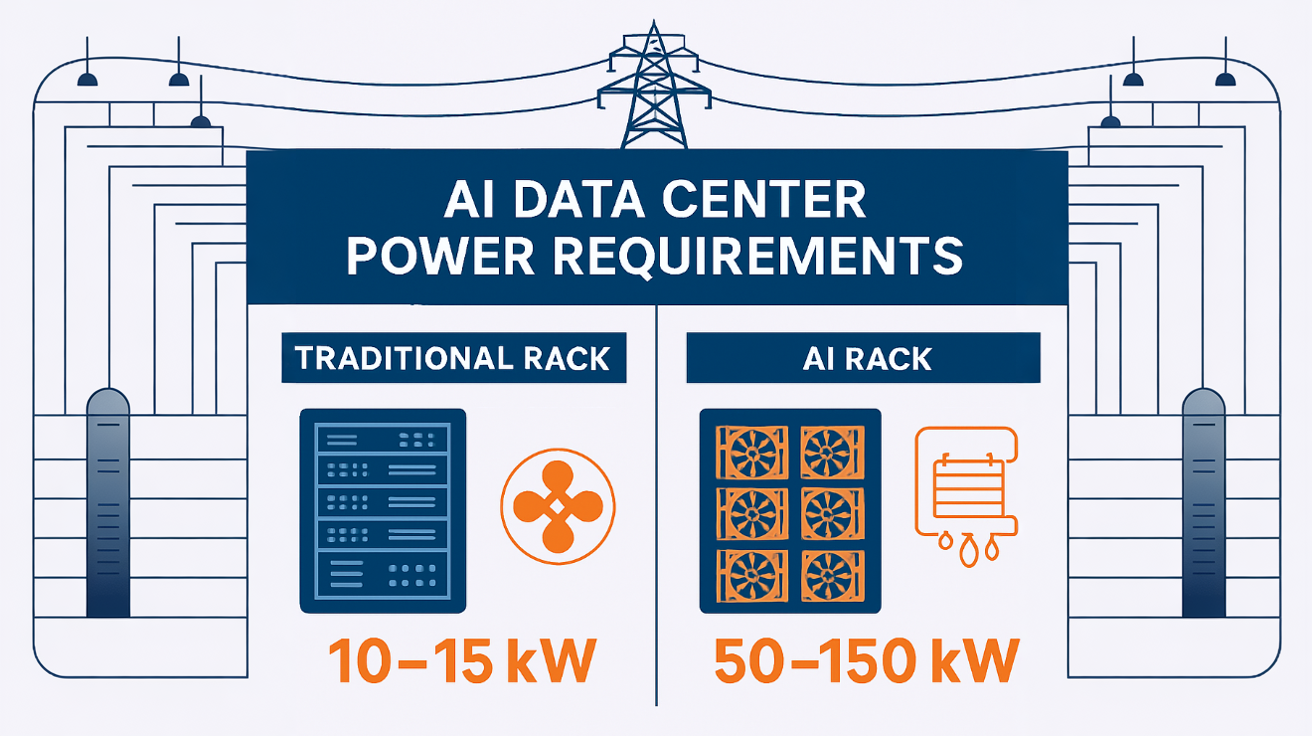
- Key Challenge: Power availability has become the primary constraint, with AI facilities requiring 50-150kW per rack versus 10-15kW for traditional computing.
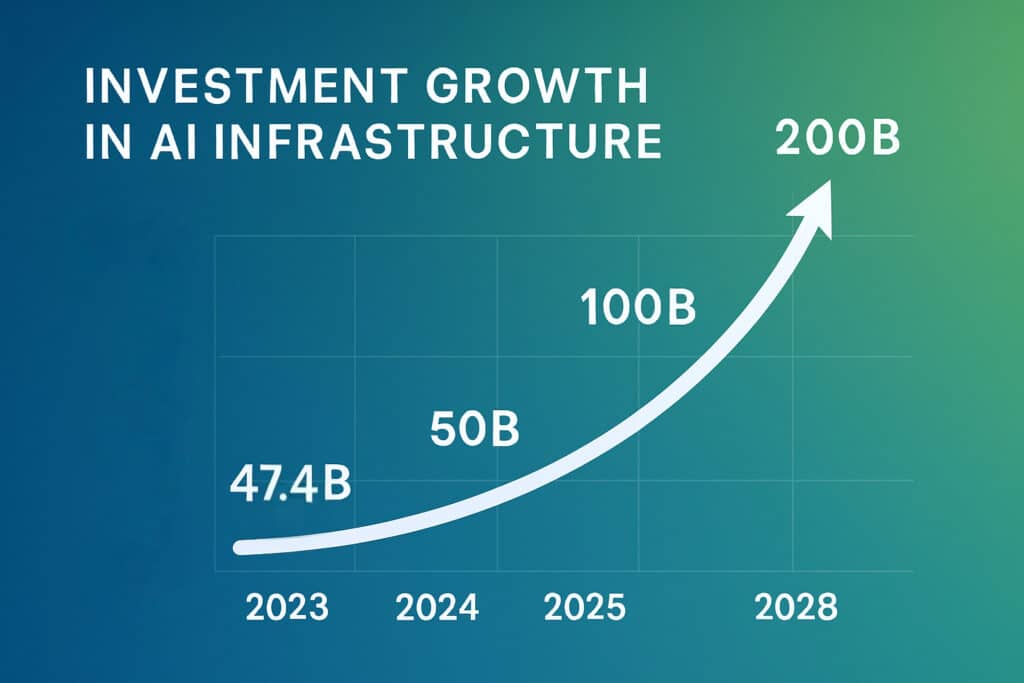
- Market Size: AI infrastructure spending reached $47.4B in H1 2024 and is projected to exceed $200B by 2028.
The artificial intelligence revolution has triggered an unprecedented infrastructure gold rush. IDC reports that organizations increased spending on AI infrastructure by 97% year-over-year in the first half of 2024, reaching $47.4 billion and setting the stage for what analysts predict will be a $200 billion market by 2028. Behind this explosive growth lies a fundamental question: what companies build data centers for AI, and how are they reshaping the backbone of modern computing?
The answer reveals a complex ecosystem where traditional tech giants, specialized infrastructure providers, and innovative newcomers are all racing to meet unprecedented demand. With massive hyperscale investments reaching unprecedented levels, the landscape of AI-ready facilities represents one of the most significant infrastructure transformations in modern history. Success in this space increasingly depends on comprehensive digital infrastructure solutions that can address both computational and energy challenges.
Who Are the Major Players Building AI Data Centers?
Hyperscale Cloud Providers: The Infrastructure Titans
The largest technology companies have committed staggering resources to AI data center development. Microsoft leads this charge, announcing plans to invest $80 billion in fiscal 2025 specifically for AI-enabled data centers, with over half of this investment targeted for U.S. infrastructure. This represents nearly double their total capital expenditure from just four years ago.
Amazon Web Services continues its massive expansion despite recent project reassessments, while Google’s parent company Alphabet has similarly committed tens of billions to AI infrastructure. Meta has joined this investment race, focusing particularly on facilities designed for large language model training and inference workloads that require sustained, high-density computing power.
These hyperscalers face unique challenges in their AI data centers power requirements. Unlike traditional computing workloads that peak and valley throughout the day, AI operations demand constant, maximum-capacity performance. This has forced these companies to rethink everything from power distribution to cooling systems, often requiring facilities that can handle 200 megawatts or more of continuous load.
GPU Cloud Specialists: The New Infrastructure Category
A new breed of companies has emerged specifically to address AI workload demands. These “neocloud” providers focus exclusively on delivering GPU-as-a-Service solutions optimized for artificial intelligence applications. CoreWeave exemplifies this category, having raised over $12 billion in funding and positioning itself as an “AI hyperscaler” with 28 operational data centers by the end of 2024.
Crusoe Energy Systems has taken a unique approach, building massive AI campuses powered entirely by renewable energy. Their $3.4 billion joint venture with Blue Owl Capital demonstrates how specialized providers are attracting significant institutional investment for AI-specific infrastructure development. This aligns with growing industry recognition that renewable energy for data centers provides both cost stability and sustainability benefits.
Lambda Labs represents another important player in this space, offering both cloud services and on-premises solutions for AI developers. These companies typically maintain closer relationships with NVIDIA and other chip manufacturers, often securing priority access to the latest GPU technologies that larger cloud providers may not prioritize for their diverse customer bases.
Traditional Data Center Operators: Adapting for AI Demands
Established colocation providers like Digital Realty and Equinix have rapidly evolved their offerings to support AI workloads. These companies bring decades of experience in data center operations, existing relationships with enterprises, and established presence in key markets worldwide. However, they’ve had to make significant investments in power infrastructure, cooling technologies, and facility designs to meet AI requirements.
Equinix has emphasized the importance of interconnected AI-ready infrastructure, noting that AI workloads require different types of data centers depending on the phase of operation. Their platform approach connects hyperscale facilities for training, colocation facilities for data privacy, and edge locations for inference workloads.
Digital Realty has partnered with several GPU cloud providers, including CoreWeave, to offer specialized AI hosting solutions. Their global footprint and established utility relationships provide crucial advantages in markets where power availability has become the primary constraint for AI infrastructure development.
How Do AI Data Centers Differ from Traditional Facilities?
Power Density and Energy Requirements
AI data centers operate at power densities that would have been unimaginable just five years ago. Where traditional facilities might support 10-15 kilowatts per rack, modern AI installations require 50-150 kilowatts per rack to accommodate dense GPU configurations. This fundamental shift has forced infrastructure providers to completely rethink electrical distribution, cooling systems, and facility design.
The most advanced AI facilities now feature specialized power delivery systems, including high-voltage distribution and direct current power supplies that improve efficiency while reducing space requirements. These technical innovations have become competitive differentiators, with some providers achieving 95% power usage effectiveness ratings through careful engineering and renewable energy integration.
Cooling Innovation and Thermal Management
Traditional air cooling systems simply cannot handle the thermal loads generated by modern AI hardware. Leading providers have implemented liquid cooling technologies, including direct-to-chip cooling and immersion systems that can manage heat loads of 150 kilowatts per rack or higher. These systems not only improve performance but also reduce overall energy consumption by 30-40% compared to air cooling.
The most sophisticated installations combine multiple cooling approaches, using precision airflow management for standard equipment while deploying liquid cooling for high-density AI clusters. This hybrid approach allows facilities to support diverse workloads while maintaining optimal efficiency for each application type.
Top 10 Companies Building AI-Ready Data Centers
Based on investment levels, technological capabilities, and market presence, here are the leading companies reshaping AI infrastructure:
- Microsoft – The Redmond giant is leading hyperscale investment with $80 billion commitment for fiscal 2025, focusing heavily on AI-enabled infrastructure to support OpenAI partnerships and Azure growth.
- CoreWeave – This specialized GPU cloud provider with $19 billion valuation operates 28+ facilities globally, positioning itself as an “AI hyperscaler” focused exclusively on machine learning workloads.
- Amazon Web Services – The cloud computing leader plans massive global expansion with $100+ billion investment over the next decade, building new capacity across multiple U.S. states and international markets.
- Google/Alphabet – The search giant has committed to major AI infrastructure investments with $75 billion capex commitment for 2025, primarily focused on servers and data centers to support Gemini AI development.
- Crusoe Energy Systems – This innovative company builds renewable-powered AI campuses with $3.4 billion joint venture funding, specializing in sustainable data centers that can house up to 100,000 GPUs.
- Digital Realty – This traditional colocation provider has successfully adapted its global portfolio for AI workloads, partnering with GPU cloud specialists to offer specialized hosting solutions across key markets worldwide.
- Equinix – The interconnection leader operates a global platform optimized for AI workload distribution, connecting hyperscale facilities for training with edge locations for inference workloads.
- Oracle – The enterprise software company has made strategic partnerships and direct infrastructure investments, notably working with specialized providers on major AI campus developments.
- Meta – The social media giant has announced focused AI training facilities with $65 billion investment commitment for 2025, including plans for a massive 2+ gigawatt data center.
- Lambda Labs – This specialized provider offers both cloud services and on-premises AI infrastructure solutions, maintaining close relationships with chip manufacturers for priority access to latest GPU technologies.

Regional Development Patterns and Geographic Strategy
The geographic distribution of AI data center development reveals strategic thinking around power availability, regulatory environment, and market access. Northern Virginia remains the global epicenter, though power constraints have pushed development toward emerging markets in Texas, Ohio, and other regions with abundant energy resources.
International expansion has accelerated, with providers establishing significant presences in Europe and Asia-Pacific. CoreWeave’s recent expansion into the UK and Norway demonstrates how AI infrastructure follows renewable energy availability and favorable regulatory frameworks. Similarly, Crusoe’s partnerships with Nordic data center operators reflect the importance of sustainable power sources for long-term AI operations.
What Are the Key Infrastructure Requirements for AI Data Centers?
Power Infrastructure and Grid Integration
The power requirements for AI data centers extend far beyond what traditional grid infrastructure can typically support. Most AI facilities require dedicated substations, often involving utility partnerships that take years to develop and implement. The most successful providers have established relationships with power authorities and integrated renewable energy development into their site selection process.
Grid interconnection has become the primary bottleneck for AI infrastructure development. Wait times for power connections in popular markets like Northern Virginia now exceed five years, forcing providers to explore alternative approaches including on-site generation, energy storage, and strategic partnerships with renewable energy developers. The most successful providers understand that choosing the right digital infrastructure provider requires evaluating power-first development capabilities rather than traditional location factors.
Site Selection and Development Considerations
Modern AI data center development prioritizes power availability above traditional location factors like proximity to population centers. The most valuable sites feature access to abundant renewable energy, transmission infrastructure capacity, and streamlined regulatory environments that facilitate rapid development timelines.
Water availability has emerged as another critical constraint, particularly for facilities employing liquid cooling systems. Leading providers now conduct comprehensive environmental assessments that include groundwater access, municipal supply capacity, and wastewater treatment capabilities as part of their site evaluation process.
Technology Integration and Future-Proofing
The rapid evolution of AI hardware requires infrastructure designed for adaptability rather than specific configurations. The most advanced facilities feature modular designs that can accommodate future chip architectures, cooling requirements, and power densities without major reconstruction projects.
Network infrastructure represents another crucial consideration, with AI workloads requiring ultra-low latency connections between compute clusters and high-bandwidth links to storage and data sources. Leading providers implement redundant fiber connections, software-defined networking, and direct cloud connectivity to ensure optimal performance for diverse AI applications.
What Does the Future Hold for AI Infrastructure Development?
Market Projections and Investment Trends
Industry analysts project that AI infrastructure spending will surpass $200 billion by 2028, driven by continued enterprise adoption and increasingly sophisticated AI applications. This growth trajectory suggests that current capacity constraints will persist, creating opportunities for innovative infrastructure providers who can deliver solutions faster than traditional development timelines.
Private equity investment has become a major factor in AI infrastructure development, with firms like Blackstone committing billions to specialized providers. This institutional capital has accelerated development timelines and enabled providers to secure GPU inventory and power resources that might otherwise be unavailable.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Environmental concerns are reshaping AI infrastructure development, with enterprises increasingly requiring carbon-neutral or carbon-negative solutions for their AI workloads. This has elevated renewable energy integration from a nice-to-have feature to a fundamental requirement for many large-scale AI deployments.
The most forward-thinking providers are developing energy campuses that combine renewable generation, storage, and AI computing in integrated systems. These approaches not only address sustainability requirements but also provide cost stability and energy security that traditional grid-dependent facilities cannot match. Understanding comprehensive energy solutions for data centers has become essential for meeting the growing demands of AI workloads while maintaining operational efficiency.
The Infrastructure Foundation for Tomorrow’s AI Economy
The race to build AI-ready data centers represents more than just a technology infrastructure buildout. It’s a fundamental reimagining of how we power, cool, and connect the computing resources that will define the next era of digital innovation. From hyperscale giants investing tens of billions to specialized providers developing renewable-powered campuses, the companies building these facilities are creating the foundation for applications we can barely imagine today.
The winners in this infrastructure race will be those who can deliver not just raw computing power, but integrated solutions that address power constraints, sustainability requirements, and the rapid evolution of AI technology itself. As the demand for AI infrastructure continues its explosive growth, the strategic decisions made by these providers today will determine which companies can capitalize on tomorrow’s opportunities.
For organizations evaluating their AI infrastructure strategy, partnering with providers who understand both the technical requirements and the energy challenges of modern AI computing has become essential. Hanwha Data Centers specializes in developing comprehensive energy solutions for digital infrastructure, helping clients navigate the complex landscape of AI-ready facility development with expertise in renewable energy integration and strategic site development.
Frequently Asked Questions
What companies are leading AI data center development globally?
Microsoft leads with $80 billion in planned investment for fiscal 2025, followed by specialized providers like CoreWeave and traditional operators like Digital Realty and Equinix who have adapted their offerings for AI workloads.
How much power do AI data centers require compared to traditional facilities?
AI data centers typically require 50-150 kilowatts per rack compared to 10-15 kilowatts for traditional computing, with some facilities requiring 200+ megawatts of total capacity for large-scale AI operations.
Why are companies building dedicated AI data centers instead of using existing facilities?
AI workloads require specialized power distribution, advanced cooling systems, and network configurations that most existing facilities cannot support without major modifications.
What role does renewable energy play in AI data center development?
Renewable energy has become essential for AI infrastructure due to sustainability requirements, cost stability, and the need for reliable power sources in constrained grid markets.
How long does it take to build an AI-ready data center?
Development timelines vary significantly based on power availability and site readiness, ranging from 18 months for specialized providers to 5+ years in constrained markets requiring new utility infrastructure.




