The convergence of AI, data explosion, and infrastructure transformation represents the largest technology shift since the internet’s commercialization.
- Global data center power demand will grow 165% by 2030, while $6.7 trillion in infrastructure investment is needed
- AI workloads create dramatically higher power density requirements, with GPU clusters consuming up to 80kW per rack and facilities requiring continuous high-performance operation
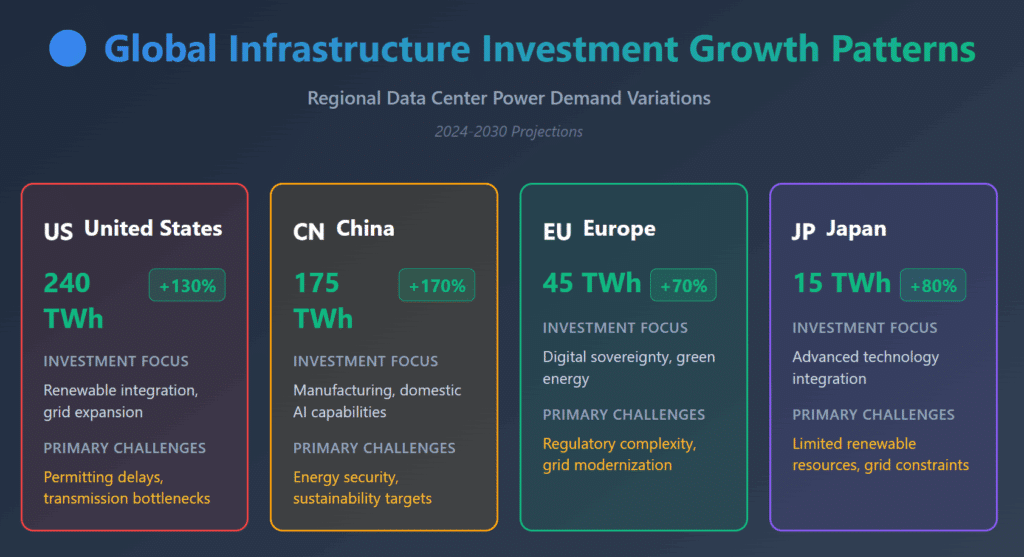
- Data center power demand growth is concentrated in the U.S. (240 TWh increase), China (175 TWh), and Europe (45 TWh), requiring fundamental changes in energy sourcing and distribution
- Geographic distribution strategies are shifting from proximity-based to power-first approaches, with renewable energy access becoming the primary site selection criterion
Organizations that secure reliable, scalable infrastructure partnerships today will dominate tomorrow’s AI-driven economy.
The influx of artificial intelligence is creating the most significant infrastructure transformation in modern history. Global power demand from data centers will increase by 165% by the end of the decade. Data centers will require $6.7 trillion worldwide by 2030 to keep pace with AI compute needs. This convergence of artificial intelligence capabilities, exponential data growth, and the infrastructure solutions required to support both represents a defining moment for businesses, investors, and entire economies.
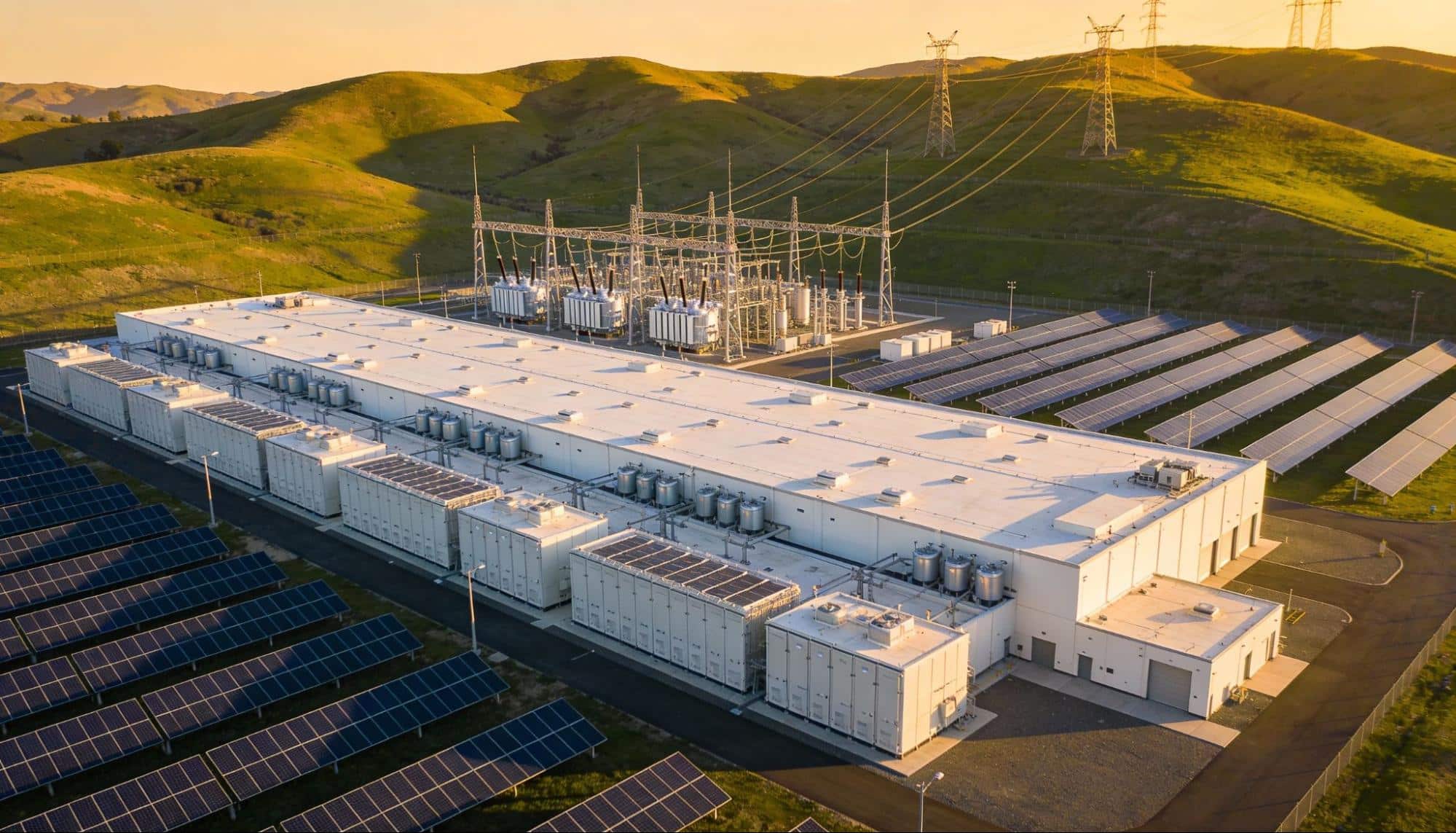
The scale of this transformation extends far beyond incremental improvements to existing systems. We’re witnessing a fundamental restructuring of how digital infrastructure is conceived, financed, and deployed. Traditional data centers that consumed 30 megawatts are being replaced by AI-optimized facilities demanding 200 megawatts or more. Power density in data centers will grow from 162 kilowatts per square foot to 176 kilowatts per square foot by 2027. The energy for AI data centers has become the critical bottleneck that will determine which organizations can scale their capabilities and which will be constrained by physical limitations.
The Scale of Energy for AI Data Infrastructure
AI-specific infrastructure will require $5.2 trillion in capital expenditures by 2030, while traditional IT applications will need an additional $1.5 trillion. These figures add up to nearly $7 trillion in total infrastructure investment over the next five years.
Data generation is accelerating at equally dramatic rates. Global data center electricity consumption could reach 945 terawatt-hours by 2030. AI workloads are driving much of this growth, requiring substantially more energy per query than traditional web applications.
Predictions say that 40% of existing AI data centers will be operationally constrained by power availability by 2027. The growth of hyperscale data centers to implement generative AI is creating demand for power that will exceed utility providers’ ability to expand capacity fast enough. This mismatch between AI compute needs and available infrastructure creates unprecedented challenges and massive opportunities for forward-thinking infrastructure developers.
Why Are AI Compute Needs Reshaping Infrastructure?
AI compute needs differ from traditional IT workloads because they require continuous high-performance computing rather than intermittent processing. Unlike conventional enterprise applications that peak and decline throughout the day, AI training sessions and inference operations often run continuously for weeks or months. This sustained operation creates entirely new categories of infrastructure demands.
The power density requirements alone represent a paradigm shift. Modern AI facilities demand power densities that push the boundaries of traditional electrical distribution systems. GPU clusters used for AI training can consume upwards of 80 kilowatts per rack, creating demands that traditional facilities weren’t designed to handle. These extreme densities need different approaches to power distribution, cooling systems, and facility design.

Emerging Geographic and Water Infrastructure Strategies
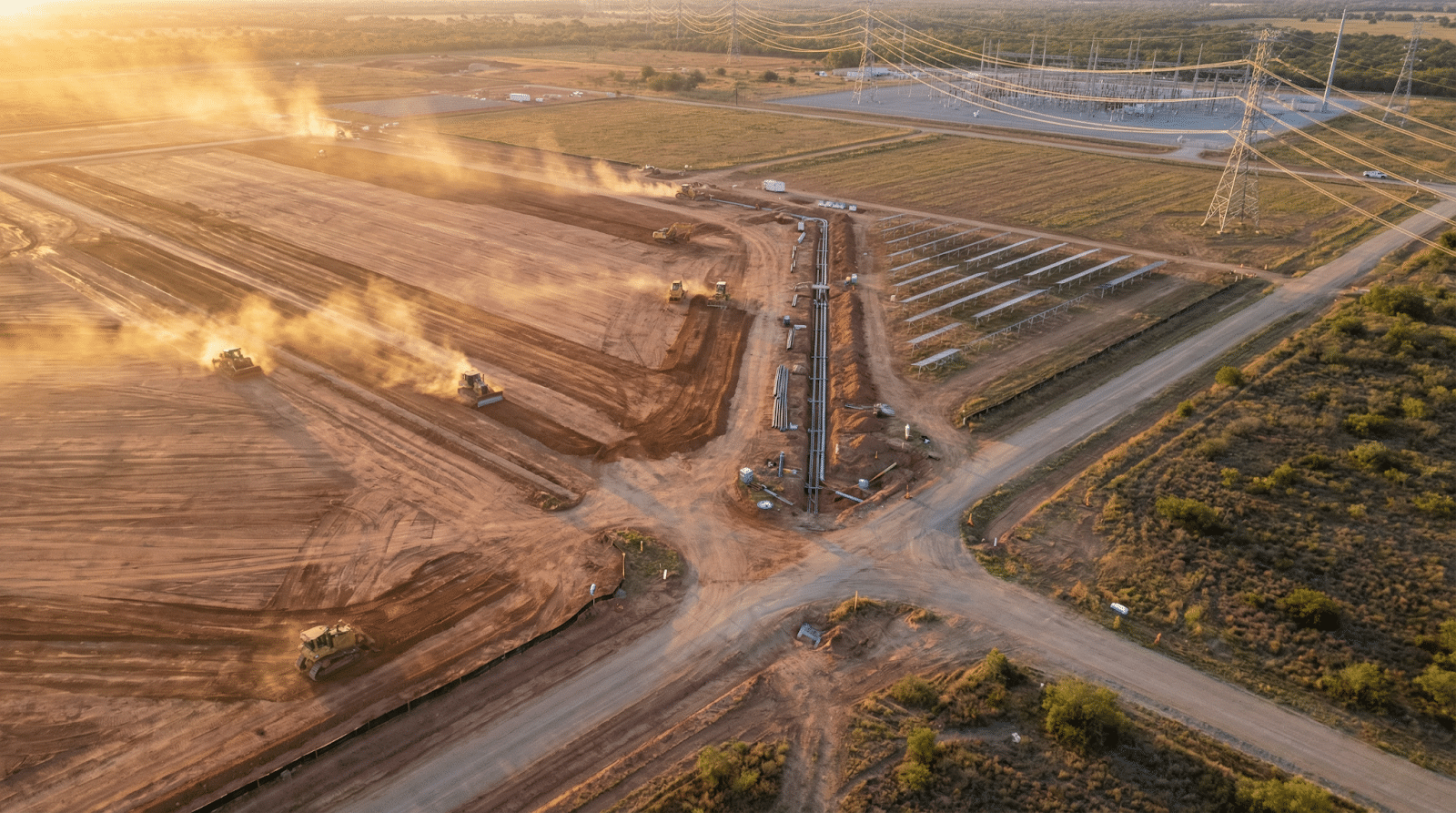
Geographic distribution strategies are evolving in response to these new requirements. Traditional data center locations were chosen based on proximity to metropolitan areas, existing fiber infrastructure, or favorable real estate costs. Today’s AI infrastructure developers prioritize power availability above all other factors. Secondary markets outside major technology hubs are experiencing unprecedented data center investment as hyperscalers follow available renewable energy resources.
Water infrastructure has emerged as an equally critical factor in AI data center site selection. Advanced cooling systems required for high-density AI workloads consume substantial water resources, with large facilities using millions of gallons daily. Site viability now depends on securing reliable water supplies, establishing appropriate wastewater management systems, and obtaining necessary water rights before breaking ground. Markets with abundant water resources and existing treatment infrastructure are gaining competitive advantages in attracting AI data center investment.
The dual requirements of power and water availability are fundamentally reshaping geographic patterns in data center development. Sites must provide access to both gigawatt-scale power and adequate water infrastructure, a combination that eliminates many traditionally attractive locations. This convergence is driving development toward markets that can deliver comprehensive utility infrastructure rather than just one critical resource.
How Is Data Driving Infrastructure Innovation?
Exponential data growth is forcing infrastructure innovation beyond simple storage capacity increases. Modern AI systems require access to massive datasets for training, real-time data streams for inference, and sophisticated data pipelines that can process information at unprecedented scales and speeds.
Data volume growth is creating new infrastructure requirements at every level. Training large language models requires access to datasets measured in terabytes or petabytes, stored across distributed systems that can deliver consistent high-throughput access to thousands of GPUs simultaneously. The infrastructure required to support these data workflows includes high-speed networking, advanced storage systems, and sophisticated data management platforms.
Real-time processing requirements are equally demanding. AI applications serving millions of users require infrastructure that can process queries with millisecond response times while maintaining consistent performance under varying loads. This powerful computing demands intelligent load balancing, distributed caching, and edge computing capabilities that can adapt dynamically.
The geographic distribution of data processing is creating new infrastructure patterns. While some AI workloads benefit from centralized processing in massive facilities, others require distributed edge infrastructure that can process data closer to its source. This hybrid approach requires coordinated planning across multiple layers, from hyperscale training facilities to edge computing nodes deployed in smaller markets.
What AI Infrastructure Trends Are Driving Investment?
Investment flows are concentrating on five critical infrastructure trends. Understanding these trends provides insight into where the most significant opportunities and challenges will emerge over the next decade.
5 Critical Infrastructure Trends Transforming the AI Economy
1. Renewable Energy Integration: The push toward sustainable power is becoming a competitive necessity rather than just an environmental goal. Major technology companies are making substantial commitments to renewable energy to meet sustainability targets and secure predictable long-term power costs.
2. Power-First Geographic Strategy: Site selection is shifting toward power availability considerations. Traditional location factors like proximity to population centers are giving way to power-first strategies that prioritize access to renewable resources and existing transmission infrastructure.
3. Water Infrastructure for High-Density Operations: The water demands of advanced cooling systems are reshaping site selection criteria. Facilities require access to millions of gallons daily, making water supply, treatment capacity, and wastewater management as critical as power availability for AI workload support.
4. Modular Infrastructure Design: The traditional approach of building massive, monolithic data centers is giving way to modular designs that can be deployed incrementally as demand grows. This approach reduces initial capital requirements while providing flexibility for future expansion.
5. Grid Modernization and Storage: The integration of battery storage systems and smart grid technologies is becoming essential for managing the variable power demands of AI workloads while maintaining grid stability and reducing dependence on fossil fuel backup systems.

What Are the Economics of This Infrastructure Intersection?
The economic implications of AI, data, and infrastructure extend across multiple sectors and investment categories. Understanding these financial flows provides insight into where the most significant opportunities and risks are emerging.
| Infrastructure Investment Category | 2025-2030 Investment (Trillions) | Primary Drivers |
| Technology Hardware & Computing | $3.1 | GPU clusters, specialized processors, networking equipment |
| Power Generation & Distribution | $1.3 | Renewable energy projects, grid infrastructure, transmission |
| Facilities & Site Development | $0.8 | Land acquisition, construction, specialized infrastructure |
| Total AI Infrastructure Investment | $5.2 | Projected AI workload requirements |
| Traditional IT Applications | $1.5 | Non-AI data center workloads and infrastructure |
| Combined Infrastructure Investment | $6.7 | Total global data center infrastructure needs |
Source: McKinsey analysis, “The cost of compute: A $7 trillion race to scale data centers,” 2025
Regional growth patterns reveal variations in infrastructure investment and development opportunities:
| Region | Power Demand Growth (2024-2030) | Investment Focus | Primary Challenges |
| United States | 240 TWh (+130%) | Renewable integration, grid expansion | Permitting delays, transmission bottlenecks |
| China | 175 TWh (+170%) | Manufacturing, domestic AI capabilities | Energy security, sustainability targets |
| Europe | 45 TWh (+70%) | Digital sovereignty, green energy | Regulatory complexity, grid modernization |
| Japan | 15 TWh (+80%) | Advanced technology integration | Limited renewable resources, grid constraints |
Source: International Energy Agency, “Energy demand from AI – Energy and AI – Analysis,” 2024
Investment flows are concentrating in organizations that can deliver integrated solutions combining power generation, infrastructure development, and energy management capabilities. Companies building AI-ready data centers are attracting impressive levels of capital from institutional investors, sovereign wealth funds, and technology companies seeking to secure their infrastructure requirements.
What Challenges Must Organizations Navigate?
Supply chain constraints, regulatory hurdles, and sustainability requirements create the primary obstacles for AI infrastructure development.
Supply chain constraints for essential infrastructure components are creating delays and cost pressures across the industry. Constraints have arisen from supply chain bottlenecks and infrastructure that is both costly and time-intensive to upgrade.
Regulatory hurdles are complicating infrastructure development in many markets. Environmental permitting processes, grid interconnection procedures, and local zoning requirements can add years to project timelines. Organizations that can navigate these regulatory complexities while maintaining project momentum will secure significant competitive advantages.
Sustainability requirements are becoming stringent as stakeholders and regulators focus on the environmental implications of AI infrastructure growth. The challenge lies in balancing performance requirements with emissions reduction goals while maintaining cost-effectiveness and operational reliability.
What Does the Infrastructure of Tomorrow Look Like?
Emerging technologies are reshaping AI infrastructure possibilities. Green hydrogen production, small modular nuclear reactors, and advanced geothermal systems offer potential solutions for the next generation of AI facilities. Green hydrogen production and storage systems offer potential solutions for long-duration energy storage and carbon-free backup power. Small modular nuclear reactors could provide consistent baseload power specifically designed for data center loads.
Advanced geothermal technologies are showing promise for providing both power generation and direct cooling capabilities. These systems could change the economics of AI infrastructure in certain geographic markets by providing integrated energy for AI data solutions that address both power and thermal management requirements.
Policy implications are becoming increasingly apparent. Governments are recognizing that AI infrastructure will determine economic competitiveness in the coming decades. This recognition is driving new approaches to permitting, tax incentives, and public-private partnerships designed to accelerate development.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes energy for AI data centers different from traditional data centers? AI workloads require substantially more power per unit of computing compared to traditional applications, with continuous operation rather than variable demand patterns. This difference creates unique challenges for power distribution, cooling systems, and energy procurement that traditional data center designs can’t accommodate.
How are companies addressing the power constraints limiting AI data center development? Leading organizations are adopting power-first site selection strategies, investing in dedicated renewable energy projects, and implementing advanced energy storage systems. Many are also exploring secondary geographic markets with better power availability rather than competing for limited capacity in traditional technology hubs.
What role does renewable energy play in AI infrastructure trends? Renewable energy has become essential for sustainability goals and long-term cost predictability. Major AI infrastructure projects now routinely include dedicated solar or wind installations, with some facilities designed to operate entirely on renewable power combined with battery storage for continuous operation.
How long does it typically take to develop AI-ready infrastructure from planning to operation? Large-scale AI infrastructure projects face significant development timelines due to environmental permitting, power interconnection processes, construction, and commissioning phases. Projects with existing grid connections or pre-approved sites can reduce these timelines, while new developments in constrained power markets may face extended approval processes.
Building Sustainable Infrastructure for the AI Era
The intersection of AI, data, and infrastructure represents both the greatest opportunity and the greatest challenge facing technology leaders today. Organizations that secure reliable, scalable infrastructure partnerships will be positioned to capitalize on AI capabilities as they mature and expand. Those that delay infrastructure planning risk being constrained by power availability, cooling capacity, or geographic limitations just as AI becomes most valuable to their competitive positioning.
Hanwha Data Centers specializes in developing comprehensive energy solutions that address these converging infrastructure challenges. Our integrated approach combines renewable energy development, energy storage, and specialized infrastructure to create reliable, sustainable power systems for AI and data-intensive operations. Contact our team to explore how customized energy for AI data solutions can support your organization.